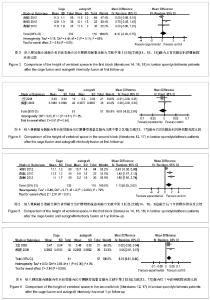
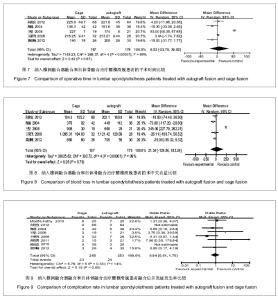
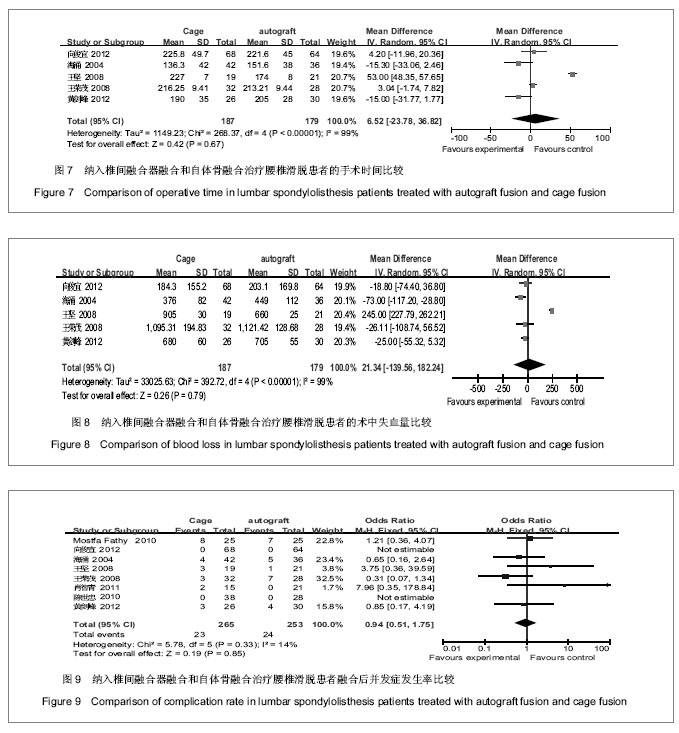
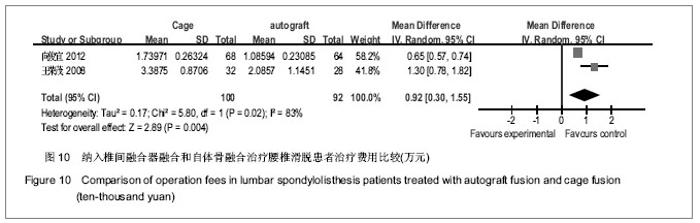
| [1] 林海,曾强,谢小平,等.经后路椎间植骨融合椎弓根钉内固定治疗腰椎滑脱[J].西部医学2010,22(18):1406-1407.[2] Zhao J, Zhang F, Chen X, et al. Posterior interbody fusion using a diagonal cage with unilateral transpedicular screw fixation for lumbar stenosis. J Clin Neurosci. 2011;18(3): 324-328. [3] Chrastil J, Patel AA. Complications associated with posterior and transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion.J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2012;20(5):283-291.[4] Yu CH, Wang CT, Chen PQ. Instrumented posterior lumbar interbody fusion in adult spondylolisthesis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2008;466(12):3034-3043. [5] Kim JS, Kang BU, Lee SH,et al. Mini-transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion versus anterior lumbar interbody fusion augmented by percutaneous pedicle screw fixation: a comparison of surgical outcomes in adult low-grade isthmic spondylolisthesis. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2009;22(2):114-121. [6] Chen SH, Lin SC, Tsai WC, et al. Biomechanical comparison of unilateral and bilateral pedicle screws fixation for transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion after decompressive surgery--a finite element analysis. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2012;13:72. [7] Vavruch L,Hedlund R,Javid D,et al . A prospective randomized comparison between the cloward procedure and a carbon fiber cage in the spine: a clinical and radiologic study. spine.2002;27(16):1694-1701.[8] 王晓东,洪曼杰,郭洲,等.椎弓根螺钉内固定及后路植骨融合术治疗腰椎滑脱[J].广东医学,2007,28(7):1081-1082.[9] Jüni P, Altman DG, Egger M. Systematic reviews in health care: Assessing the quality of controlled clinical trials. BMJ. 2001;323(7303):42-46. [10] Turek SL. Orthopaedics principles and their application Ath ed. Lippincott Company.1984;12(4):1524-1552.[11] 海涌,陈晓明,陈志明,等.后路椎间融合术治疗成人腰椎滑脱的前瞻陛研究[J].中华骨科杂志,2004,24(10):586-589.[12] 郝延科,黄向业,李凌云,等. 后路椎弓根内固定联合cage椎间融合器与髂骨块椎间融合治疗腰椎不稳症[J].中国中西医综合外科杂志,2009,15(4):413-416.[13] 肖智青,王凤龙,朱锦忠,等.椎间植骨与椎间融合器治疗腰椎滑脱的疗效比较[J].实用中西医结合临床,2011,11(4):12-13.[14] 黄剑峰,宁锦龙,岑定善,等.两种椎间融合方式在治疗腰椎滑脱症中的应用研究[J].中华临床医师杂志,2012,6(10):2819-2822.[15] 王荣茂,林翔,石树培,等. 后路椎体间自体髂骨融合与Cage融合治疗下腰椎不稳的比较研究[J].中国修复重建杂志,2008,22(8): 928-932.[16] 向俊宜,孟庆奇,赵文韬,等. 后路椎弓根钉内固定结合单纯椎间植骨融合与椎间融合器治疗腰椎不稳的疗效比较[J].广东医学, 2012,33(22):3423-3425.[17] 王坚,黄象望.不同植骨融合方法治疗退行性腰椎滑脱症的疗效评价[J].现代生物医学进展,2008,8(7):1313-1318.[18] 陈世忠.椎间融合器与单纯椎间植骨法治疗退变性腰椎滑脱症的疗效分析[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2010,25(5):439-440.[19] Fathy M, Fahmy M, Fakhri M, et al. tcome of instrumented lumbar fusion for low grade spondylolisthesis; Evaluation of interbody fusion with & without cages. Asian J Neurosurg. 2010;5(1):41-47.[20] Niggemann P, Kuchta J, Grosskurth D, et al. Spondylolysis and isthmic spondylolisthesis: impact of vertebral hypoplasia on the use of the Meyerding classification. Br J Radiol. 2012;85(1012):358-362. [21] 曹正春,郑闽前,张爱梁.后路复位植骨内固定治疗腰椎滑脱的临床观察[J].实用骨科杂志,2007,13(11):689-690.[22] Brantigan JW, McAfee PC, Cunningham BW, et al. erbody lumbar fusion using a carbon fiber cage implant versus allograft bone. An investigational study in the Spanish goat. Spine (Phila Pa 1976).1994;19(13):1436-1444. [23] González-Darder JM. Development of the anterior cervical postdiscectomy arthrodesis: bone graft, plate, intersomatic cage and plate-cage. Neurocirugia (Astur). 2006;17(2):140-147. [24] 雷高,罗德民,薛厚军,等.半限制型与非限制型假体在颈椎间盘置换中的应用[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(9):1635-1638.[25] 邓字骁,洪瑛,刘浩,等.椎间盘置换中体位对假体置入后活动度的影响[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(39):7221-7226. |